Fine Beautiful Info About How To Cure A Plugged Ear

In some cases, this treatment may make the condition worse.
How to cure a plugged ear. How to relieve pressure when you have a middle ear infection: This may help reduce swelling and congestion that could be causing blockages. Take a nasal decongestant for up to 3 days.
Warm 2 to 3 tablespoons of your oil of choice, but be careful not to make it too hot. Using a nasal spray can relieve sinus blockage and inflammation, which can ultimately help unplug your ears. You can typically treat the causes of ear pressure at home through swallowing, yawning to “pop” your ears, or taking otc medications.
Using a nasal steroid spray is one of the best remedies, says dr. Keep the head tilted for a few seconds, then return to an upright position. If symptoms continue, contact your doctor.
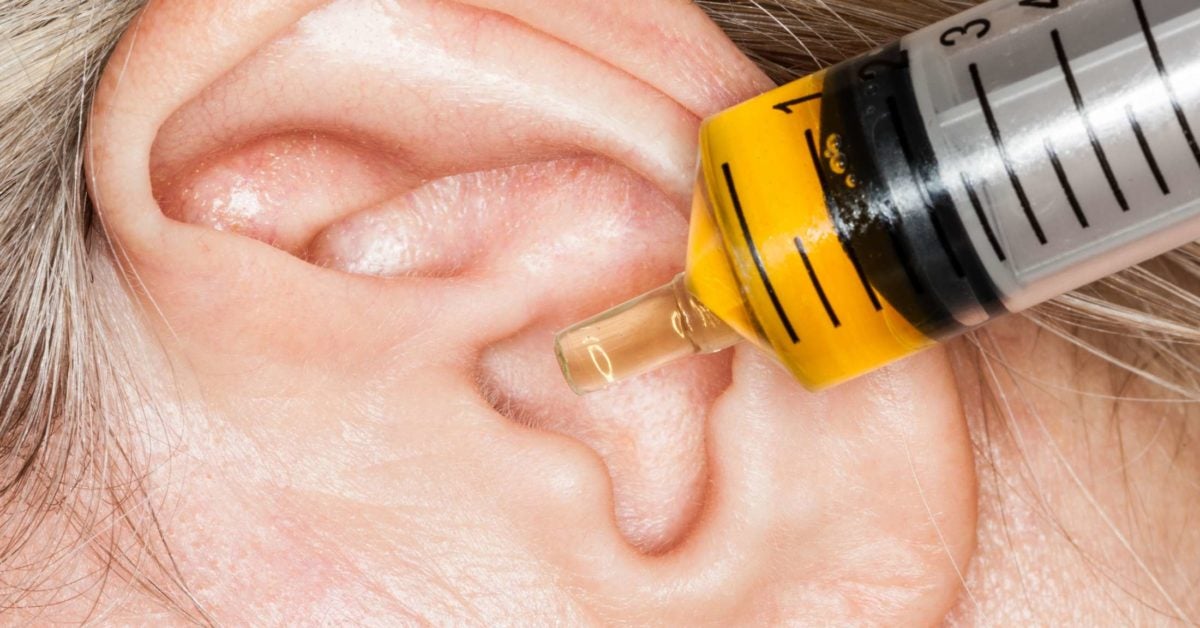
Hydrogen peroxide (3%): You may need to see an ear, nose and throat specialist for treatment. This results in pressure changes, and sometimes, the accumulation of fluid in the ear.
All you need to do is swallow while pinching your nose shut. No stronger than 3%, or else you might damage your ear. Try dripping mineral, olive, or baby oil into your clogged ear.
Another way on how to open a blocked ear is by doing the toynbee maneuver. According to the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc), most sinus infections resolve. Just be sure you’re using the nasal spray correctly by aiming it.
Loopearplugs.com has been visited by 10k+ users in the past month If decongestants or antihistamines do not provide relief, contact your doctor. Then, use an eye dropper to put one to two drops in your ear.
Check it on your hand or wrist to make sure it’s a safe temperature and doesn’t irritate your skin. How to test the temperature of water. Use a saline spray.
Download article 1 recognize the symptoms. Mix in equal parts hydrogen peroxide and water. The wax should soften and flush from the ear.
A common course of treatment for eustachian tube dysfunction is the use of decongestants or antihistamines. Whether from cold, allergies, or infection, swelling will prevent eustachian tubes from opening and allowing air to pass. When this happens, you will feel the following symptoms: